HER-2 Overexpression in Gastric and Gastroaesophageal Cancer: A Different Disease among Gastric Adenocarcinoma Subtypes
ADVANCED RESEARCH IN GASTROENTEROLOGY & HEPATOLOGY JUNIPER PUBLISHERS
Authored by C Caglevic
Introduction
Gastric adenocarcinoma is currently one of the most frequent malignancies worldwide, becoming the fifth place in incidence and third place in mortality among solid tumors [1]. The geographical distribution of this disease is variable, being most common in countries with worse water quality and deficient food storage [2].
In the Pacific coast of South America, mainly in countries like Chile and Peru, probably due to a high prevalence of pathogenic Helicobacter Pylori subtypes, gastric cancer is a serious public health problem that involves a higher mortality when compared with developed countries of North America and Europe [3]. In high income countries, gastric cancer incidence has decreased during the last decades due to an important impact in environment that overlaps the genetic predisposition for this malignancy [4,5].
Despite its high frequency, gastric adenocarcinoma, unfortunately, is often diagnosed at late stages, when curative surgery cannot be performed due to the presence of unresectable tumors or to metastatic disease. First steps of this malignancy are often asymptomatic or give mild and non- specific symptoms such as abdominal discomfort, anemia, weight loss, anorexia and others, which can delay the correct and opportune diagnosis [6].
This issue has been well considered in countries such as Japan, where gastric cancer screening has become a powerful tool in order to improve early diagnosis providing real options of curative treatments and therefore diminishing mortality [7,8].
Regarding to non-metastatic locally advanced disease, different approaches to improve overall survival have been done. Despite that improving results have been achieved, several patients treated with a curative attempt will have disease recurrence and will die for this malignancy, including patients that underwent perioperative chemotherapy, post-operative radio-chemotherapy or adjuvant chemotherapy [9-11].
For metastatic gastric cancer the expected median overall survival is less than 1 year [12,13]. Since 1990´s decade clinical trials have shown overall survival benefit when palliative chemotherapy has been compared with best supportive care [13,14]. Combining different cytotoxic chemotherapy agents has shown improving results in overall survival and higher response rates when compared with single agent chemotherapy, however these results are modest and adding a third drug does not really improve results but increases toxicity [15-19].
By recent years, thanks to a better comprehension of the molecular heterogeneity and of the pathways that are involved in gastric carcinogenesis, research has focused in new approaches such as targeted therapy [20]. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER 2), also known as Cerb-2 o ERBB2, is a protooncogene located in chromosome 17 q21 that codes for this transmembrane protein that enhances a tyrosine kinase activity, conducting cell growth and differentiation [21]. HER 2 is an independent ligand that can be activated by mutations or due to overexpression of the receptor [21]. First discovered in breast cancer tumors, HER 2 mutations were found to have a worse prognosis of the disease when compared with patients that not carried such mutations [22,23]. Slamon et al. [24] shown that trastuzumab, a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody, when added to adjuvant chemotherapy regimen (doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide follow by docetaxel), in Her 2 overexpressed patients, had an enormous impact in overall survival when comparing the chemotherapy regimen without adding the monoclonal antibody (HR 0.63; p<0.001) and also the arm that received trastuzumab had benefit in disease free survival (HR 0.64; p<0,001) when compared with the control arm. Positive results were also achieved in HER 2 overexpressed breast cancer patients that underwent neoadjuvant treatment [25], and in metastatic disease when adding trastuzumab to chemotherapy or when including a double anti HER 2 blockade using also pertuzumab, other antibody that targets HER 2 overexpressed tumors [26,27].
Since recently, HER 2 mutations have been identified in several other solid tumors including ovarian cancer, prostatic cancer, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, gastric and gastroesophageal cancer as well [28].
Among gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer patients, HER 2 overexpression has been found in different proportions depending of reports, therefore this incidence fluctuates between 4 to 53%, with a median of incidence of 17,9% [28-30]. In Chile, where gastric cancer is a highly prevalent malignancy, HER 2 overexpression has been reported in the 11.9% of the patients. These findings have been reported mainly in the intestinal variety of adenocarcinoma but not in diffuse subtype patients [31].
HER 2 blockade in the first line of treatment for metastatic and unresectable gastric and gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with HER 2 overexpression:
Looking forward improving survival in metastatic gastric cancer patients that overexpress HER 2, clinical trials have been conducted.
ToGA Trial was a phase III clinical trial for the first line of treatment of advanced gastric and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinomas (unresectable locally advanced, recurrent and metastatic), restricted to patients with HER 2 overexpression in their tumors, that compared chemotherapy combination (fluoropyrimidine and cisplatin doublet) with or without adding trastuzumab [32]. This was a multicenter, open-label, randomized trial. From a total of 3807 patients that consented for participating in this study, only 810 overexpressed HER 2 (22%), and finally a total of 584 patients from Asia, America and Europe, with measurable and non-measurable disease were randomized and treated. HER 2 expression of the tumors was assessed using different criteria as used for breast carcinoma, based on a different staining pattern of immunohistochemistry, which was also validated with FISH by Hofmann, including patients with HER 2 +++ in IHC or based on HER2:CEP17 ratio of at least 2 or greater [33].
Its primary endpoint was overall survival, showing a statistically and clinically relevant difference, with a mean overall survival of 13.8 months (95% CI: 12-16) in those patients who received chemotherapy plus trastuzumab combination and 11.1 months (95% CI: 12-16) in those patients who received chemotherapy without the monoclonal antibody, with a hazard ratio of 0.74 (95% CI; 0.6-0.91 p=0.046). Secondary endpoints such as progression free survival, time to progression, duration of response and overall response rate were also higher in the trastuzumab plus chemotherapy combination group when compared with the control arm. In a post-hoc analysis, the effect on overall survival was greater on patients with higher levels of HER-2 expression (IHC 3+, IHC 2+ and FISH positive), achieving a median overall survival of 16 months versus 11 months in those with lower HER-2 expression (HER 2 1+- HER 2 negatives but FISH +). There were no differences in adverse effects between the control arm and study treatment arm, except for grade 3 infusion reactions that were higher in the trastuzumab group.
After these findings, the predictive value of HER 2 level was explored by Gomez-Martin and cols., by studying 90 patients with advanced gastric adenocarcinoma in the first-line treatment including trastuzumab, with regards of the HER2/CEP17 ratio and HER2 gene copies number (GCN), calculating a HER2/CEP17 ratio of 4.7 and GCN of 9.4 as the optimal cutoff levels for defining sensitivity to trastuzumab [34].
From a pharmacological point of view, there were differences in the calculated plasmatic clearance of trastuzumab between patients with HER-2 positive breast and gastric cancer, being higher on the latter, suggesting that a higher dose of trastuzumab would be more effective. This question was explored on a phase 3btrial (HELOISE, Hoffmann-La Roche) in the first line of treatment for gastric and gastroesophageal metastatic patients with HER 2 overexpression, that compared standard chemotherapy with two different doses of trastuzumab (loading dose of 8 mg/kg for both groups followed by 6 mg/kg intravenously every 3 weeks for control arm or 10 mg/kg intravenously every 3 weeks for the study arm). This trial was terminated because of futility demonstrated on a preplanned interim analysis [35].
Assuming the positive results previously achieved with trastuzumab, other strategies to block the HER 2 pathway were studied. The use of lapatinib, a small-molecule tyrosine kinase dual inhibitor of EGFR and HER 2, was explored in the phase III TRIO- 013/LOGiC trial, that compared chemotherapy (capecitabine plus oxaliplatin) with or without lapatinib in untreated patients with advanced or metastatic gastric, esophageal or gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with HER 2-amplification assessed by FISH or, if not available, by immunohistochemistry (IHC 3+). Unfortunately, this trial failed to show benefit in overall survival and in progression free survival when adding lapatinib in the study population. Nevertheless, in a preplanned subgroup analysis, the trial showed increased overall survival in Asiatic and in 60 years old or younger patients. Toxicity was higher in the lapatinib arm, principally more diarrhea grade 3 and higher was reported [36].
Looking forward enhancing HER 2 blockade, currently there is an ongoing phase III trial, JACOB, that compares the same study arm treatment used in ToGA trial (5FU or capecitabine, cisplatin and trastuzumab) with the addition of pertuzumab as a first line treatment for metastatic gastric and gastroesophageal gastric cancer that overexpresses HER 2. The primay end point of this study is to evaluate overall survival. Results have not been published yet [37].
Perioperative chemotherapy in HER 2 overexpressed gastric and gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with locally advanced disease
Considering the positive results of the ToGA trial, the next question to address is to evaluate if the addition of HER-2 targeted therapy in the perioperative setting can improve the outcomes in resectable - HER2 overexpressed gastric adenocarcinoma or allowing that unresectable disease to become potentially resectable in case of response. To answer this issue currently there are two ongoing clinical trials. INNOVATION trial is a randomized phase II collaborative study between EORTC and the Korean Cancer Study Group, comparing perioperative chemotherapy with fluoropyrimidine, cisplatin and trastuzumab, with or without the use of pertuzumab. Its primary endpoint is to evaluate and compare pathological complete response among study arms [38]. The other study, TRIGGER trial, is a randomized phase II trial, that compared perioperative chemotherapy with S-1 and cisplatin, with or without trastuzumab. Its primary endpoint is overall survival. [39].
Despite that there is not data yet the supports the use of HER 2 blockade in the perioperative setting, case reports have been published, most of them from Asiatic patients and centers [40-47] (Table 1).

Second line treatment blocking HER 2 for metastatic and unresectable gastric and gastroesophageal adenopatients with HER 2 overexpression
The role of HER2 blockade in the metastatic second-line treatment scenario has been explored using two different agents: lapatinib, an oral tyrosine-kinase inhibitor of HER-1 and HER-2 intracellular domains, and ado-trastuzumab-emtansine (TDM-1), a monoclonal antibody conjugated of trastuzumab and emtansine, a cytotoxic microtubule binding agent. Both have shown activity on HER2 positive breast cancer beyond the first line of treatment in metastatic disease [48-52].
The TyTAN trial was an open-label multicenter phase III trial, including Asiatic patients, who had progressed after prior chemotherapy. It compared weekly paclitaxel with paclitaxel plus lapatinib. There was no difference on overall survival, progression free survival or time to progression, showing effect only on overall response rate, which is of little clinical significance. In a subgroup analysis, there was benefit on overall survival in the IHC 3+ subgroup (median overall survival 5.6m vs 4.2m; HR, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.37 to 0.93; P 0.0176) and in Chinese population, when compared with Japanese, in median overall survival (9.7 m v 7.6 months; P 0.0351) and median progression free survival (7.2m v 4.7 months ;P 0.0077) [53].
The GATSBY trial was an open-label phase 2-3 international multicenter study, that included advanced HER-2 positive gastric cancer who had progressed after a first-line therapy. It compared TDM-1 with taxane monotherapy (paclitaxel or docetaxel). The primary end point was overall survival with no significant differences between arms [54].
Both TyTAN and GATSBY raise the question about the different role of HER-2 in the gastric adenocarcinoma biology, in contrast to breast cancer, where sequential and/or additive blockade of HER- 2 signaling have some efficacy.
Conclusion
Gastric and gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma is a frequent malignancy that has an intrinsic bad prognosis unless its diagnosis was done in very early stages. HER 2 overexpression in tumor cells represent a worse prognosis, nevertheless blocking HER 2 has been demonstrated to be useful in the metastatic setting.
As an example, here, we report the case of a 65 years old man that in 2014 consulted due to dysphagia and loss of weight. Upper endoscopy found a subcardial tumor with compromise of the gastroesophageal junction. Its biopsy reported a gastric adenocarcinoma moderately differentiated. Baseline PET CT demonstrated multiple widespread disease beyond the primary tumor, metastasis was shown in lymph nodes, adrenal, lungs, liver and in several bones. After palliative radiotherapy to bone lesions to diminish bone pain, cytotoxic chemotherapy with FOLFOX regimen was started by June 2014. During cycle 4 of this regimen HER 2 was informed by IHC as highly overexpressed, then after trastuzumab was added with a loading dose of 8 mg/kg followed by 4 mg/kg every two weeks. After cycle number 22 of FOLFOX due to periferic neuropathy regimen was changed to 5FU/ Leucovorin plus trastuzumab every two weeks. After completing a total of 35 cycles of chemotherapy (including both FOLFOX and 5FU/LV regimens) and after achieving complete response patient has undergone continue treatment with trastuzumab 6 mg/kg every 3 weeks maintaining complete response. By date 62 cycles of trastuzumab have been administered without toxicity and with evident benefit (radiological and quality of life) (Figure 1).
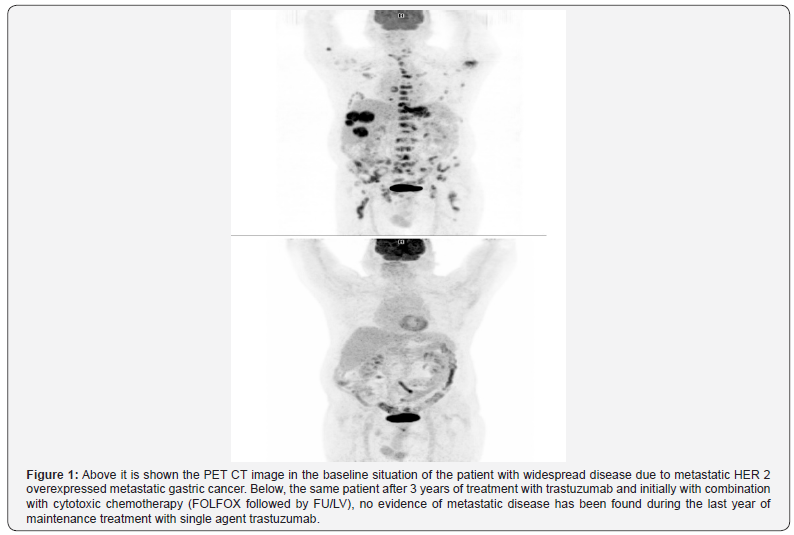
This case is an example because molecular profile, specifically HER 2, should be always be considered in the study of metastatic and or unresectable gastric cancer patients, and the use of trastuzumab in these cases should be mandatory unless contraindicated.
Despite the positive results of other HER 2 targeted treatment in the metastatic setting of breast cancer, no other targeted HER 2 blockades has shown real efficacy in gastric or gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with HER 2 overexpression.
Clinical trials that are currently ongoing probably will answer if adding HER 2 blockades to perioperative and postoperative treatment in HER 2 overexpressed gastric and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinomas will improve overall survival of these patients.
Conflict of Interest
Authors have not received funds neither any type of sponsorship and have not any conflict of interest regarding this manuscript. Dr C. Caglevic discloses: Speaker: BMS – MSD- Boehringer Ingelheim – Tecnofarma- ROCHE. Advisory and Consulting: BMS - MSD– Boehringer Ingelheim – Lilly – Astra Zeneca – Bayer. Investigator: MSD – BMS – Boehringer Ingelheim – Bayer- Roche- Astra Zeneca – Astellas- Advaxis. Travelling and educational grants: MSD – Boehringer Ingelheim, Dr C. Gallardo discloses: Travelling grants: MSD- Roche – Novartis – Eli Lilly. Advisory board: Eli Lilly – MSD.
For more articles in Advanced Research in Gastroenterology & Hepatology please click on https://juniperpublishers.com/argh/index.php
For more about Juniper Publishers please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/video-articles.php




Comments
Post a Comment