The Role of Oesophagogastroduodenoscopy in Avoiding Unnecessary Cholecystectomies in Patients with Gallstones and Upper Abdominal Discomfort_Juniper Publisher
ADVANCED RESEARCH IN GASTROENTEROLOGY & HEPATOLOGY JUNIPER PUBLISHERS
Authored by Mohamed Alshekhani
Abstract
Background: Cholelithiasis is a common condition, 10-20% of the population will develop gallstones, the incidence increases with age. Only about 30% of asymptomatic patients will wARGHant surgery during their lifetime. Dyspeptic symptoms due to other abdominal conditions such as PUD, IBS, Functional dyspepsia, IBS & GERD are frequently attributed to Gallstones.
Aim of study: To assess the role of upper endoscopy in patients with gallstones in avoiding unnecessary cholecystectomies.
Patients and methods: 124 patients were included in sulaimanyah city hospitals from October 2015 to February 2017 complaining of upper GIT symptoms and U/S evidence of gallstones and an OGD is performed to exclude other possible explanation which may avoid unnecessary operation.
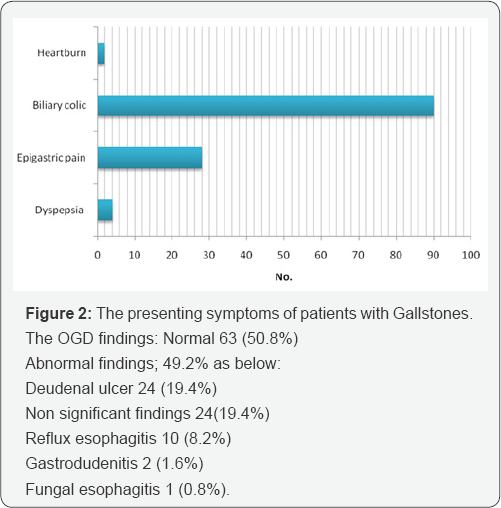
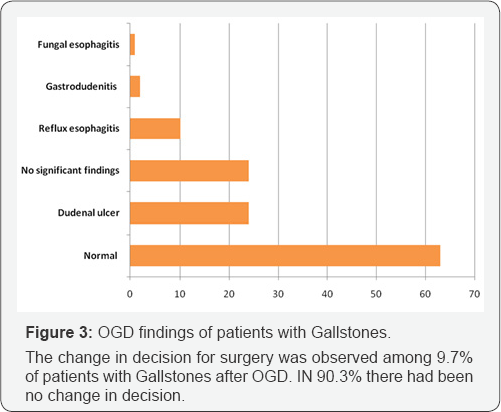
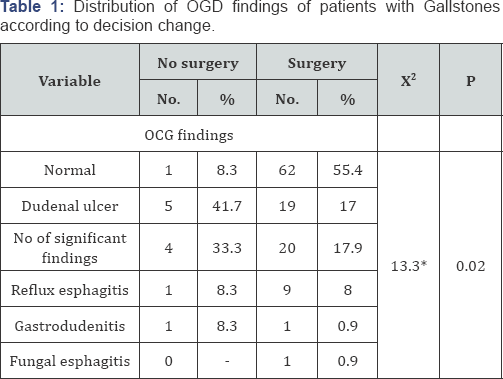
Results: Among 124 patient 99(79.8%) were females and 25(20.2%) were male; The mean age of studied patients was 46.4±14.5 years. The OGD findings of patients with Gallstones were normal 63 (50.8%), deudenal ulcer 24(19.4%), non significant findings 24(19.4%), reflux esophagi is 10(8.2%), gastrodudenitis 2(1.6%) and fungal esophagi is (10.8%), There was 12(9.6%) patients in whom surgery decision was changed while in 112(90.4%) the surgery was done.
Conclusion: OGD is a very useful tool in the preoperative evaluation of patient with Gallstones with upper GIT symptoms.
Keywords: GIT; OGD; Gallstones
Introduction
Gallstone is one of the commonest problems in GE practice [1-3]. The prevalence is 5-10% mostly among female & middle to elder age groups [4-7], rising in many countries including Iraq [8]. In England 70000 & USA > 0.5 million cholecystectomies had done each year [9]. Risk factors include; Advancing age ,Multiple pregnancies, Obesity, repeated fluctuations in body weight, rapid weight loss >1.5kg/week, high dose estrogens & Cholestyramine/fibrates [10-12]. Protective factors may include Moderate exercise, Coffee & Moderate alcohol consumption [13-15].
Presentations of Gallstones include asymptomatic& Symptomatic ones which include:
A. Biliary colic: a Moderate - Severe epigastria or right hypochondriac pain that last for 15 minutes to 6 hours or less than 24 hours , not associated with fever & can be associated with nausea/vomiting ,usually resolve spontaneously or by medications [16-18].
B.Symptomatic complications as acute pancreatitis, obstructive jaundice, cholecystitis 0.2-0.8%/ annum, 0.3-1.2% if the stones are initially asymptomatic , 0.7-2%/annum ifthe stones are initially symptomatic, Other rare symptomatic complications include Acute cholangitis, Mucocele of gallbladder, Empyema of gallbladder, Gangrenous gallbladder, Biliary peritonitis, Porcelain gallbladder, Gallbladder cancer [11,19,21,22].
Management includes:
A.Nonsurgical: Oral dissolution with bile acids successfully dissolved gallstones in an extremely limited patient population, especially in patients with symptomatic radiolucent gallstones <15 mm within a functioning gallbladder.
B. Laproscopiccholecystectomy (LC): results in a shorter hospital stay, speedier recovery, reduction of postoperative pain & better cosmetic results compared with open surgery [12,23-25].
Indications for cholecystectomy for asymptomatic Gallstones may include:
a. Age: children & young adults.
b. Very large stones >3cm.
c. Thick walled gallbladder >0.3cm.
d. Porcelain gallbladder
e. Large sessile polyps.
f. Race related like native American Indians [13,26-30].
4. Patients and Methods
A prospective study in sulaimanyahgovermental hospitals (KCGH, Shar teaching hospital & Surgical teaching hospital). A total number of 124 patients with U/S diagnosed GSs & upper GIT symptoms were referred to do OGD. A full history &clinical exam cARGHied out with emphasis on upper GIT & Biliary symptoms. Patients were followed out to see in how many patients the decision to do operation was changed in the short term follow- up of our study period. Inclusion criteria: any adult with U/S evidence of GSs & upper GIT symptoms.
Exclusion criteria: any case of complicated Gallstone including common bile duct stones, acutecholecystitis, pancreatitis, cholangitis.
Results
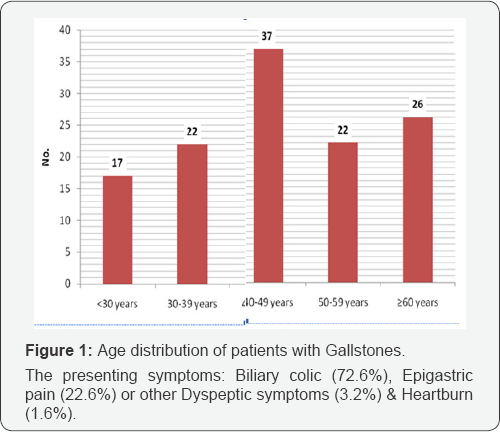
The mean age of studied patients was 46.4±14.5 years, 29.9% of them were 40-49 years, 21% of them >60 years, 17.7% ,3039 years, 17.7% ,50-59 years & 13.7% ,>10 years. Females were more than males with female to male ratio as 3.96:1(Figures 1-5 and Table 1).
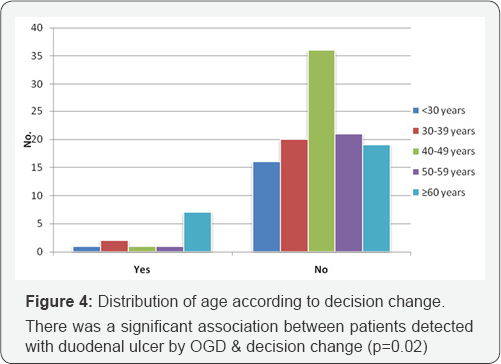
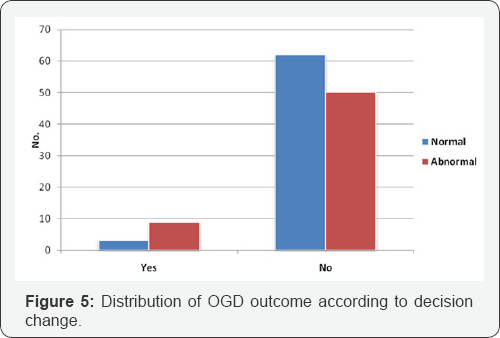
There was a significant association between Gallstone patients with abnormal OGD findings & decision change (p=0.002).
Discussion
Our patients were 124 in number, female 99 (79.8%), 25(20.2%) and a female to male ratio of 3.96/1, similar prevalence observed in a study cARGHied out in India [31-36]. In our study the OGD findings of patients with upper GIT symptoms and Gallstone were normal 63(50.8%), deudenal ulcer 24(19.4%), non significant findings 24(19.4%), reflux esophagi is 10(8.2%), gastrodudenitis 2(1.6%) and fungal esophagi is (0.8%). The results were near to results of a study cARGHied out by Thybusch et al in Germany, which showed 50% of patients had pathological findings on OGD examination [37]. Another study in Germany recommend that OGD must be done before an elective cholecystectomy &showed that out of 960 patients for elective cholecystectomy, 589 underwent gastro copy 56% had normal gastro copy [38].
In our study the change in decision for surgery was observed among 9.7% of patients with upper GIT symptoms and Gallstones after OGD while 90.3% of them had no change in decision &underwent operation. The results of OGD findings changed decision in the management plan in 8.3% and 11.7% of patients in previously mentioned study by Thybusch et al. [37] & Rassek et al. [38]. A study in Poland showed that Pathological findings were identified in 1187(42%) patients & the surgery was delayed for patients with ulcers until they finished their medical treatment , Sixteen patients had complete resolution of symptoms after medical treatment therefore cholecystectomy was not performed [39,40]. In a study done in Sudan included 108 patients with GSs & OGD was done revealed different pathological findings in 61(56%), Cholecystectomy was done for 82(76%) & 26 were treated conservatively [41]. A study in India [42] showed that in 89 patients the management plan had to be changed in 7.9% of patients based on the upper GI endoscopy findings (P value <0.001). In a meta-analysis of 12 cohort studies a total of 6317 patients with Cholelithiasis underwent OGD & in 36.3% abnormality was found in OGD but only 3.8% of patient surgery was avoided [43]. Another study by Yavorski et al. [43] recommend that patients who present with Cholelithiasis & atypical abdominal pain undergo preoperative OGD, as they found that at least 9 per cent of the patients in their study had significant findings that altered their management. In a study in india in 2016 ,216 patient with Gallstone underwent OGD, showed 100% who underwent LC, had relief of symptoms in patients with normal OGD finding while those with significant OGD findings either not went through surgery in 10(4.6%) or when surgery was done they had more gradual relief of symptoms in 6 months follow-up [44]. A study in England suggested that OGD should be considered as a routine investigation before LC especially in those, who present with overlapping upper GI symptoms [45].
Conclusion
1. Gallstones are frequently silent & upper GIT symptoms can be attributed to other pathologies in upper GIT.
2. OGD is a very useful tool which can be used in every case with Gallstone & upper GIT complains especially those with atypical symptoms.
3. OGD before elective cholecystectomy can help avoid unnecessary surgeries.
4. Biliary colic was the most important symptom that predicted negative OGDs & led to the decision of proceeding to surgery, so every effort should be done to take a good history of typical biliary colic in those patients.
For more articles in Advanced Research in Gastroenterology & Hepatology please click on https://juniperpublishers.com/argh/index.php
For more about Juniper Publishers please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/video-articles.php




Comments
Post a Comment